If you're unsure about anything related to wireless backup cameras, you're in the right place. This blog is covering everything from how they work and the ease of installation to signal stability, image quality, and common issues. Whether you're considering purchasing one or looking to maximize the performance of your current setup, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision and enhance your driving safety.
How Does The Wireless Backup Camera Work?
A wireless backup camera system transmits video footage captured by the camera mounted at the rear of the vehicle to the in-vehicle display via radio waves. The camera uses wireless RF technology to send the signal, which is received by a receiver in the display unit, showing a live feed of the area behind the vehicle. This setup helps drivers see obstacles while reversing, offering easy installation without the need for complex wiring.

Ease of Installation
Wireless backup camera systems are much easier to install compared to wired systems, as they do not require running long cables from the rear camera to the monitor. The camera and display connect wirelessly, making the setup quick and suitable for DIY installation. In contrast, wired systems involve more complex installation, requiring physical wiring through the vehicle, which often necessitates professional assistance. This makes wireless systems a more convenient and time-saving option, especially for those looking for a hassle-free solution.
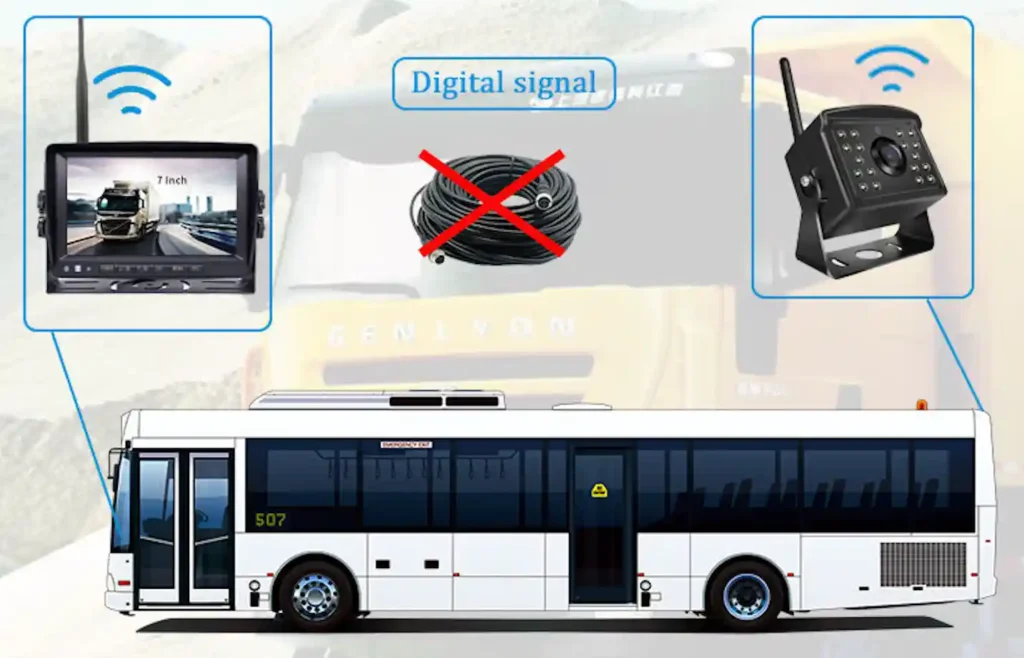

Signal Stability
Now wireless technology is much improved. the distance is from the beginning 50 meters up to now 500 meters long. In case when you face a weak signal, there are a different strong antenna for options. You can choose according to your needs.
Wireless technology has significantly improved over the years, enhancing the signal stability of backup camera systems. Initially, the transmission range was limited to around 50 meters, but modern systems can now transmit up to 500 meters. In cases where you may encounter weak signals, there are various strong antenna options available to boost the signal strength. You can select an antenna that best suits your needs, ensuring reliable performance even in more challenging environments. This flexibility makes wireless backup camera systems highly adaptable for different vehicle types and use cases.



Image Quality
The resolution of backup cameras can vary between different types, such as CVBS and AHD. CVBS cameras, while common, offer standard definition, which may not provide the clarity required in all situations. On the other hand, AHD (Analog High Definition) cameras have become increasingly popular due to their superior image quality, providing much clearer and sharper visuals, especially in high-definition formats. AHD cameras are particularly beneficial in low-light or high-contrast environments, making them a preferred choice for many users.
Here is a comparison format of CVBS and HD cameras.
| Monitor Specification | AHD Monitor | CVBS Monitor |
| Resolución | 1024xR.G.Bx600 | 800xR.G.Bx480 |
| Luminosidad | 450cd/m² | 450cd/m² |
| Contraste | 500:1 | 500:1 |
| Frecuencia de trabajo | 2400-2483,5MHZ | 2400-2483,5MHZ |
| Distancia efectiva | 500 metros en campo abierto | 150 meters in the open field |
| Entradas de vídeo | 4 canales | 4 canales |
| Impermeable | IP69K | IP69K |
| Sistema de TV | NTSC/PAL (cambio automático) | NTSC/PAL (cambio automático) |
| Fuente de alimentación | DC12V-36V | DC12V-36V |
| Modulación | 16QAM/QPSK/BPSK | FSK/GFSK |
| Mirror Flip | No espejo, espejo, flip, flip espejo | No espejo, espejo, flip, flip espejo |
| Retraso | 200ms | 200ms |
| Operation Temp | -20℃~70℃, RH 95%MAX | -20℃~70℃, RH 95%MAX |
| Storage Temp | -40℃~80℃, RH 95%MAX | -40℃~80℃, RH 95%MAX |
| Camera Specification | AHD Camera | CVBS Camera |
| Sensor de imagen | 1/2.7'' CMOS SC2235 | 1/3" CMOS PC3089 |
| Resolución | 1920x1080 pixels | 756 × 504 pixels |
| Retraso | 130 ms | 130 ms |
| Distancia IR | 15m | 15m |
| Impermeable | IP69K | IP69K |
| Fuente de alimentación | DC10V-48V | DC10V-48V |
| Operation Temp | -20℃~70℃, RH 95%MAX | -20℃~70℃, RH 95%MAX |
| Storage Temp | -40℃~80℃, RH 95%MAX | -40℃~80℃, RH 95%MAX |
Power supply
- Monitor Power Supply: The monitor typically draws power from either the vehicle's fuse box or the ignition line. This ensures that the monitor is powered on when the vehicle is running and turns off automatically when the vehicle is off, preventing unnecessary power consumption.

- Camera Power Supply: There are three main options for powering the camera:
a. Rechargeable Battery: The camera can be connected to the additional mobile lithium battery.
( please note that as the capacity of the battery is limited, typically can work 15-20 hours after being fully charged )

b. Reverse Light: Many cameras are connected to the reverse light, so they only activate when the vehicle is in reverse, conserving energy and extending the camera's lifespan.
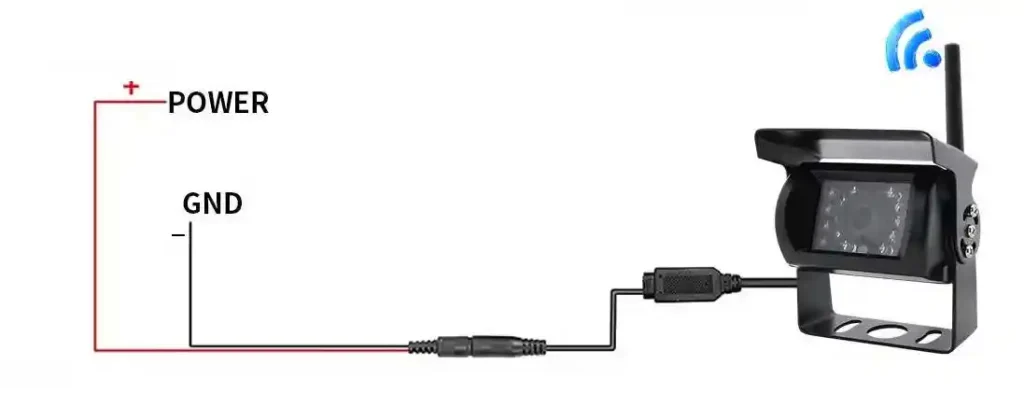
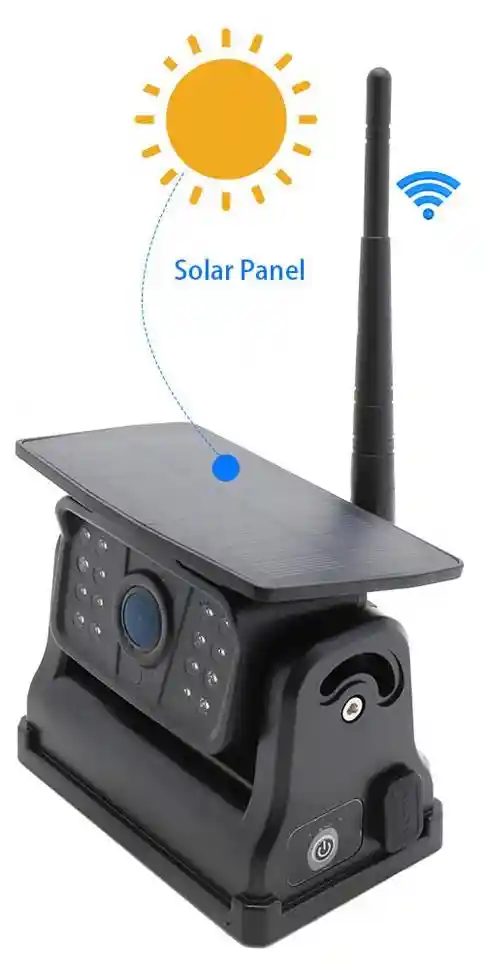
c. Solar Charging: Some modern systems offer the convenience of solar-powered cameras, which can recharge through solar panels. This option reduces the need for external power connections and is ideal for vehicles frequently exposed to sunlight, offering an eco-friendly, maintenance-free solution.

Use Cases
For vehicles like tractors, forklifts, and construction machinery, wireless cameras offer great flexibility. These vehicles frequently change their working environments, and wireless cameras provide an adaptable and mobile-friendly solution for improving rear visibility in tough working conditions.
Cost and Value
The cost of a wireless camera system typically ranges from $80 to $120, while wired camera systems cost around $50 to $80. Although wireless systems may appear more expensive upfront, the installation process for wired systems is more complex, as it requires routing cables through the vehicle. This means labor costs must also be factored in, which can range from $100 to $300 depending on factors such as vehicle type and installation complexity. Overall, while wireless systems may have a higher initial price, they are easier to install yourself (DIY), making them a more cost-effective option in the long run.
Common Issues and Solutions
- “No Signal” on the Display
If the screen shows "no signal," this may be due to a pairing failure or a loose antenna connection. Here are two methods to resolve the issue:- Method 1: Press the pairing button on the monitor again. The monitor should display "pairing is counting down." Once the countdown begins, power the camera, and the camera’s image should appear on the monitor within a few seconds.
- Method 2: Double-check that the antenna is properly attached to both the monitor and the camera. A loose connection can interfere with the signal.
- Can I Add Two More Cameras?
Yes, most wireless monitors can support up to four cameras. However, it's always a good idea to confirm this with your supplier to ensure compatibility with your specific system. - Poor Image Quality on the Monitor
If the monitor is displaying poor image quality, consider the following steps:
Ensure that no wireless devices or obstacles are interfering with the camera system’s signal.
Dirt or smudges on the camera lens can reduce image clarity. Gently clean the lens to restore clear visuals. - Black Screen on the Monitor
A black screen likely indicates that either the monitor or the camera is not powered on. Double-check that both are correctly connected to the ignition line or fuse and that the power source is functioning properly. - What is the Transmission Distance Between the Wireless Monitor and Camera?
The typical transmission range for most wireless camera systems is around 150 meters in an open field. However, VisionSafety's wireless camera systems can reach up to 500 meters. For more details and a specific range of capabilities, feel free to contact our experts. - Camera Disconnects Intermittently
If the camera disconnects or turns off randomly, this could be due to an unstable power supply or a weak connection between the camera and its power source. Double-check the wiring to ensure all connections are secure. If the camera is battery-powered, replace or recharge the batteries. For cameras connected to the reverse light, ensure proper wiring to avoid power fluctuations. - Night Vision Not Working
If the night vision mode on the camera fails to activate in low-light conditions, this might be a sensor issue or power supply problem. Ensure the camera’s infrared (IR) LEDs are functional and that nothing is obstructing the sensor. Check if the camera is receiving adequate power, as some systems may not function correctly in night vision mode without sufficient power. - Monitor Brightness Too Low
If the monitor appears too dim, making it difficult to view images during the day, the brightness settings may need adjustment.
Conclusión
If you’re looking for an excellent wireless backup camera system, we recommend Visionsafetys. We have an extensive catalog of wireless systems, ranging from 4.3 inches to 12.3 inches. We have no minimum order quantity and offer samples before order placement. For additional information and to get a customized quote, Contact Us Now!


